Spinal cord injury
(D1)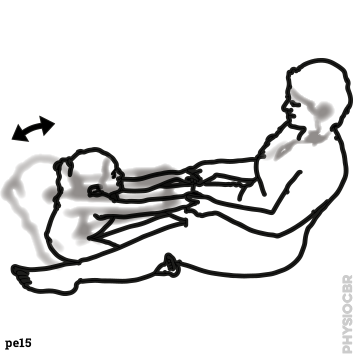
Neuromuscular
(D2)
Poliomyelitis
(D3)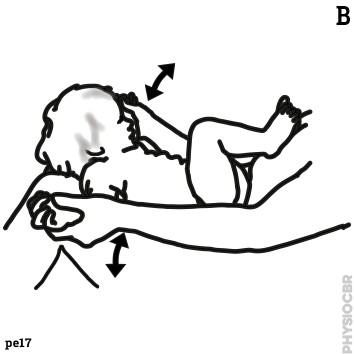
Erbs Palsy
(D4)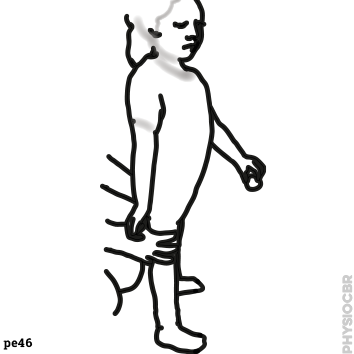
Spastic Quadriplegia
(D6)
Spastic Diplegia
(D7)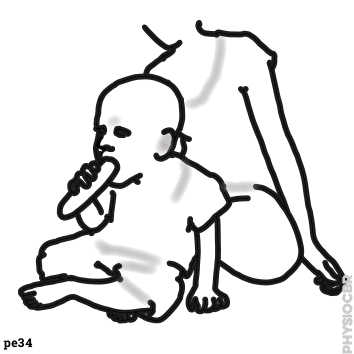
Low tone CP
(D8)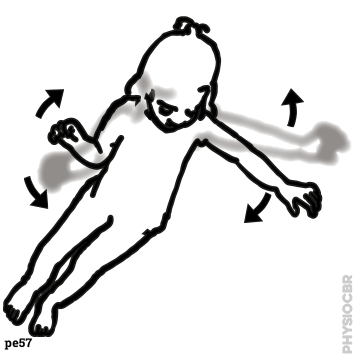
Inuit Exercises
(useful local treatment)
(not yet done)

done by parent and child
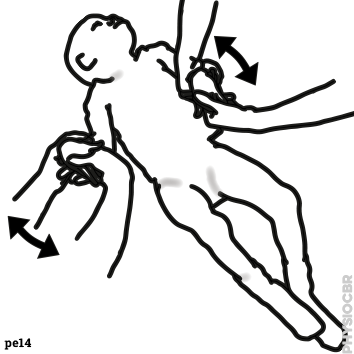
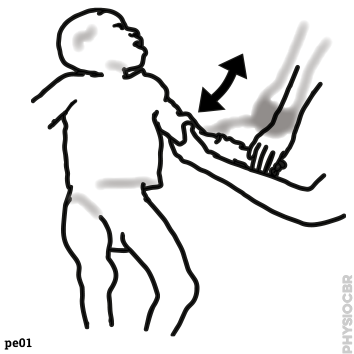
| 1 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Move feet and knees through the available range | 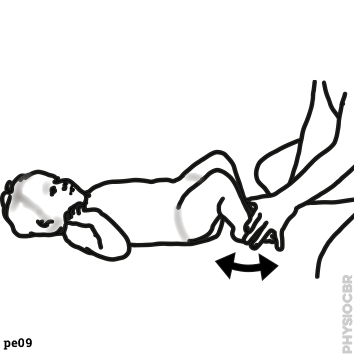 |
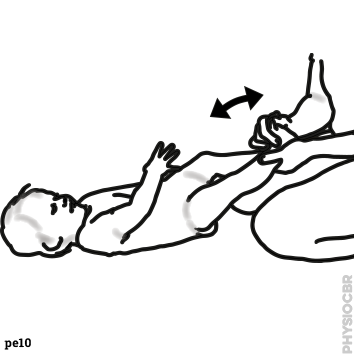 |
| 3 | Move legs through the available range, if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range. depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required | 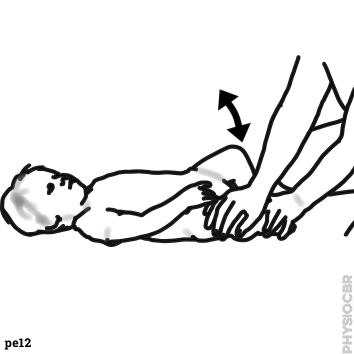 |
 |
| Neuromuscular condition | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
1: Hold the stretch for 30 counts and repeat. | |
 |
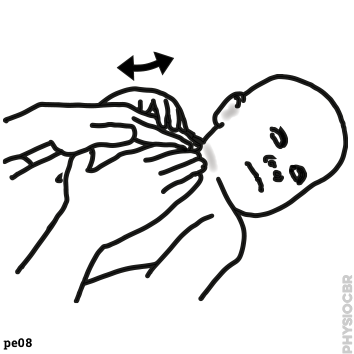
2: Decrease tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand. | |
 |
 |
3: Increase tone in elbows and improve upper limb movement. |
 |
 |
4: Sitting balance. |
 |
 |
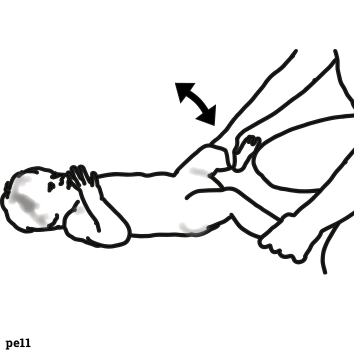
5: Move feet and knees through the available range |
 |
6: depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required... if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range | |
 |
 |
7: Chest physiotherapy techniques |
| D3: Acute poliomyelitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1: When kneeling, help child to place one leg in front and stay still for 10 secs. Then, supporting hips, help child to stand up fully, with knees straight. | ||
 |
 |
 |
 |
2: Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand | |
 |
 |
3: Sitting balance |
 |
 |
4: Move feet and knees through the available range |
 |
 |
5: Move legs through the available range and hold appropriate to where long or short leverage is required... if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range |
| D4: Erbs Palsy | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
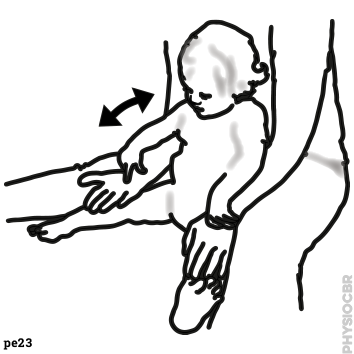
1: Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilise child’s forearm whilst moving the hand | |
 |
 |
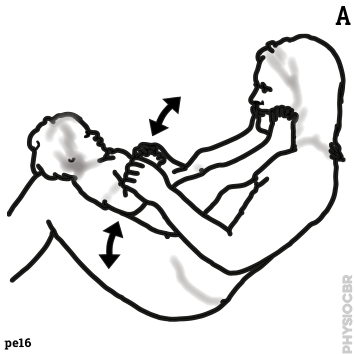
2: Increasing tone in elbows |
 |
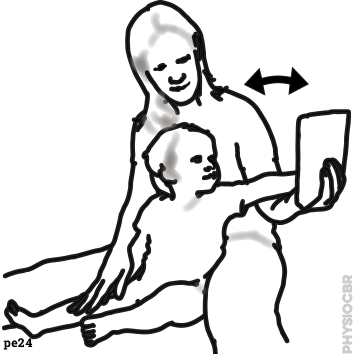 |
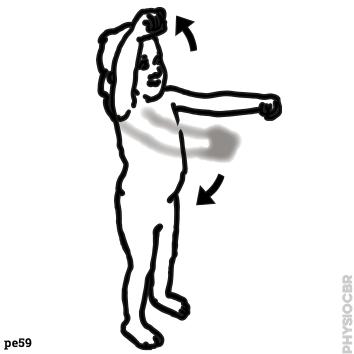
3: Encouraging arm movement with reaching |
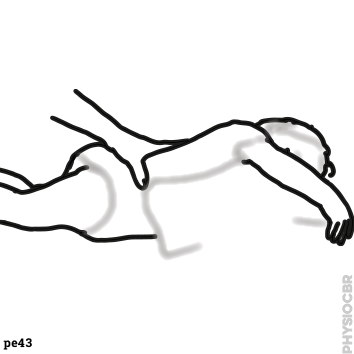
| 4: Sleep positioning | ||
 |
 |
 |
| Inuit | ||
|---|---|---|
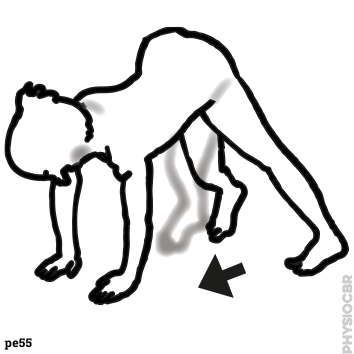
| 1: Increasing tone in limbs |  |
 |
| 2: Encouraging arm movement with reaching | 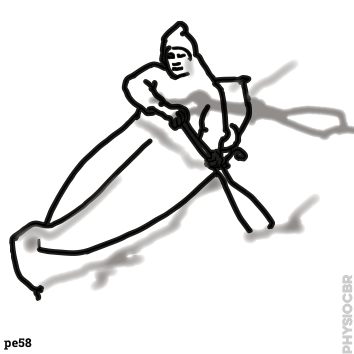 |
 |
| 3: Reaching positions | 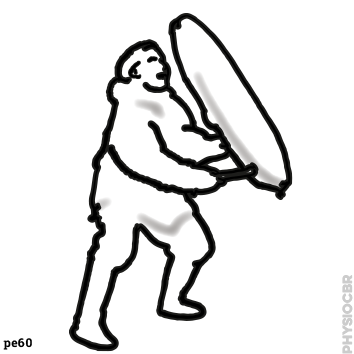 |
 |
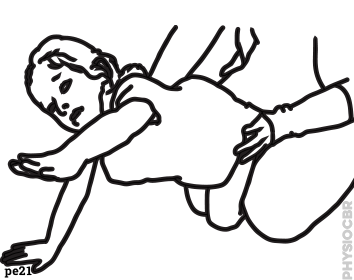
| 1 | Support child's hips whilst in crawling position and with straight elbows, for 10 seconds...Continue to support and ask child to raise one arm forward. Repeat both sides | 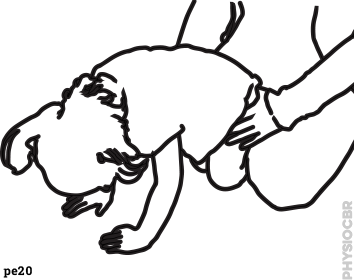 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | When kneeling, help child to place one leg in front and stay still for 10 secs. Then, supporting hips, help child to stand up fully, with knees straight. |  |
 |
 |
|||
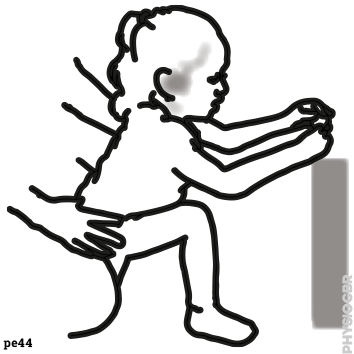
| 3 | Seated on low furniture or parent's lap, ask the child to lean forwards and then stand up. Support the child at the hips. Repeat 5-10 times or as per tolerance. | 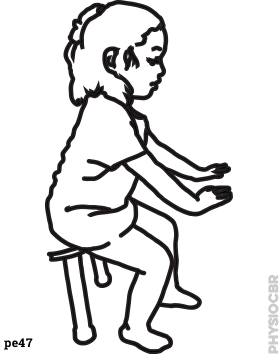 |
 |
| 4 | While lying down, encourage the child to sit using weight on forearm, placing your hand behind their opposite shoulder... help the child to sit up slowly, taking weight through their own hand | 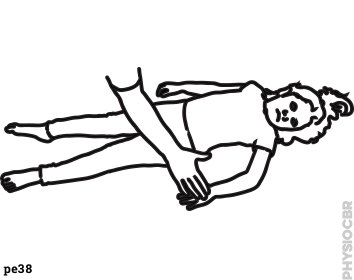 |
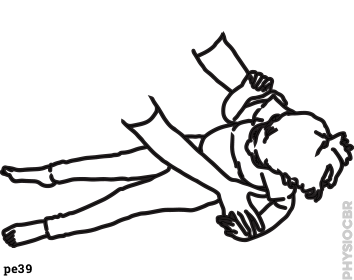 |
 |
|||
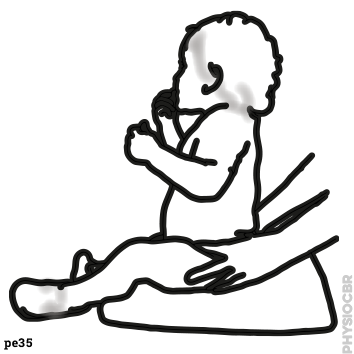
| 5 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 7 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 8 | Increasing tone in elbows |  |
 |
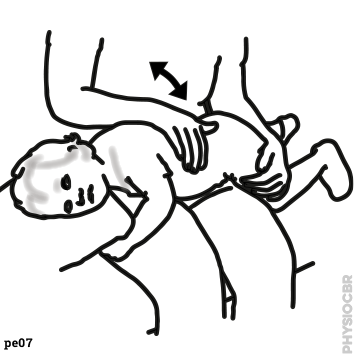
| 9 | Sitting balance |  |
 |
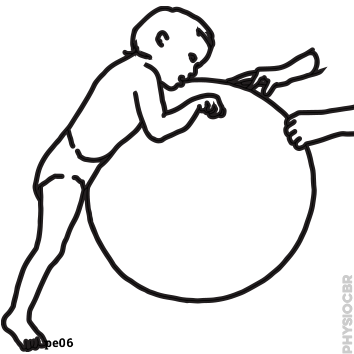
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 11 | Standing and reaching | 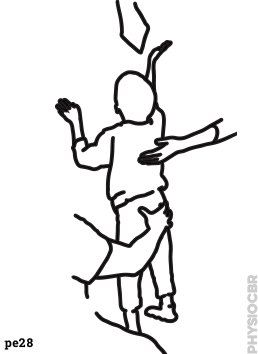 |
 |
| 13 | Standing frame | 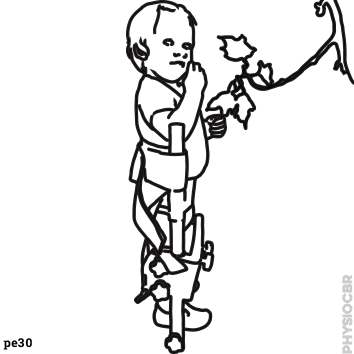 |
 |
| 14 | Standing frame alternatives | 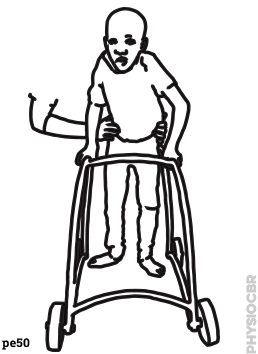 |
 |
| 15 | Stretch the elbow by gently straightening the arm... if resistance occurs, pause before continuing when it has lessened |  |
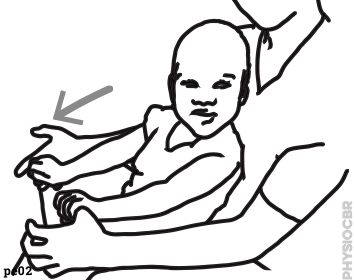 |
| 16 | Stretching on the wedge | 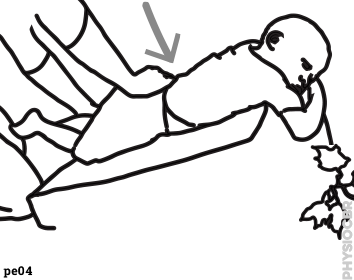 |
|
| 17 | Encourage hip flexion with supported walking | 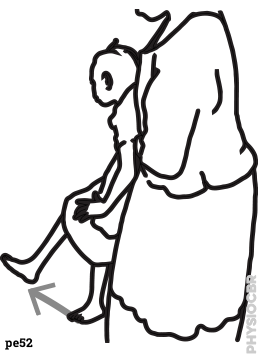 |
|
| 18 | Move feet and knees through the available range |  |
 |
| 19 | Move feet and knees through the available range, depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required...if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range |  |
 |
| 22 | Improving upper limb movement |  |
 |
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength | 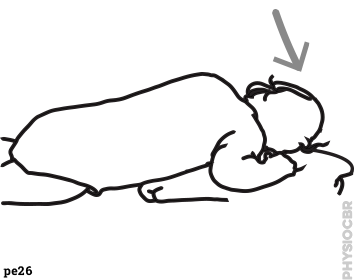 |
 |
| 25 | Resting positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
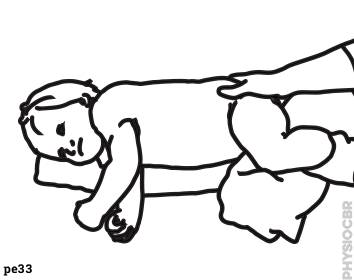
| 26 | Sleeping positions | 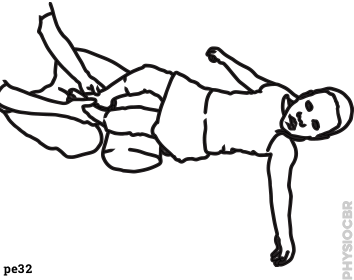 |
 |
 |
|||
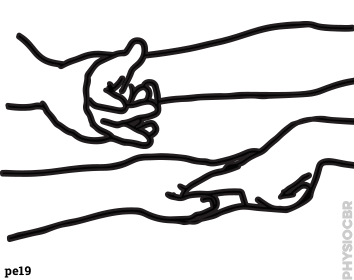
| 28 | Strengthening upper limbs | 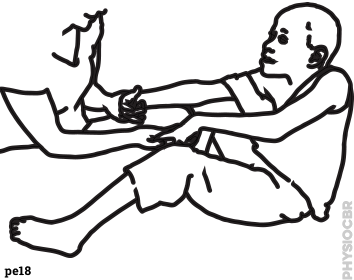 |
 |
| 29 | Strengthening lower limbs | 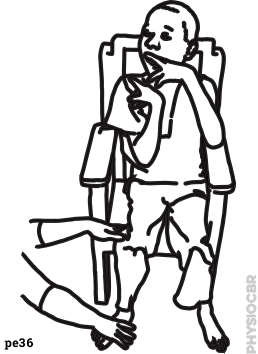 |
 |
 |
|||
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible | 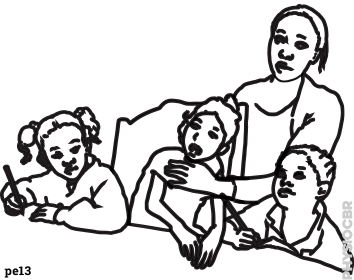 |
|
| 1 | Support child's hips whilst in crawling position and with straight elbows, for 10 seconds...Continue to support and ask child to raise one arm forward. Repeat both sides |  |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | When kneeling, help child to place one leg in front and stay still for 10 secs. Then, supporting hips, help child to stand up fully, with knees straight. |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 3 | Seated on low furniture or parent's lap, ask the child to lean forwards and then stand up. Support the child at the hips. Repeat 5-10 times or as per tolerance. |  |
 |
| 4 | While lying down, encourage the child to sit using weight on forearm, placing your hand behind their opposite shoulder... help the child to sit up slowly, taking weight through their own hand |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 5 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 7 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 8 | Increasing tone in elbows |  |
 |
| 9 | Sitting balance |  |
 |
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 11 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
| 13 | Standing frame | 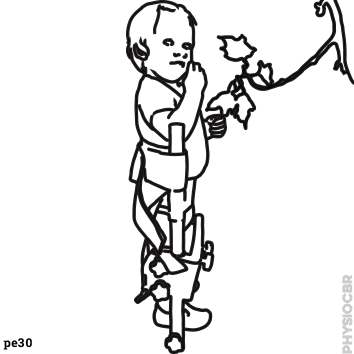 |
 |
| 14 | Standing frame alternatives |  |
 |
| 15 | Stretch the elbow by gently straightening the arm... if resistance occurs, pause before continuing when it has lessened |  |
 |
| 16 | Stretching on the wedge |  |
|
| 17 | Encourage hip flexion with supported walking |  |
|
| 18 | Move feet and knees through the available range |  |
 |
| 19 | Move feet and knees through the available range, depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required...if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range |  |
 |
| 22 | Improving upper limb movement |  |
 |
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength |  |
 |
| 25 | Resting positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 26 | Sleeping positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 28 | Strengthening upper limbs |  |
 |
| 29 | Strengthening lower limbs |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible |  |
|
| 1 | Support child's hips whilst in crawling position and with straight elbows, for 10 seconds...Continue to support and ask child to raise one arm forward. Repeat both sides |  |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | When kneeling, help child to place one leg in front and stay still for 10 secs. Then, supporting hips, help child to stand up fully, with knees straight. |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 3 | Seated on low furniture or parent's lap, ask the child to lean forwards and then stand up. Support the child at the hips. Repeat 5-10 times or as per tolerance. |  |
 |
| 4 | While lying down, encourage the child to sit using weight on forearm, placing your hand behind their opposite shoulder... help the child to sit up slowly, taking weight through their own hand |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 5 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 7 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 8 | Increasing tone in elbows |  |
 |
| 9 | Sitting balance |  |
 |
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 11 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
| 13 | Standing frame | 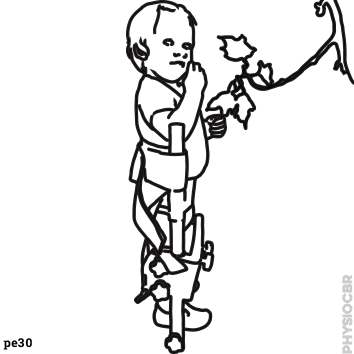 |
 |
| 14 | Standing frame alternatives |  |
 |
| 15 | Stretch the elbow by gently straightening the arm... if resistance occurs, pause before continuing when it has lessened |  |
 |
| 16 | Stretching on the wedge |  |
|
| 17 | Encourage hip flexion with supported walking |  |
|
| 18 | Move feet and knees through the available range |  |
 |
| 19 | Move feet and knees through the available range, depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required...if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range |  |
 |
| 22 | Improving upper limb movement |  |
 |
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength |  |
 |
| 25 | Resting positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 26 | Sleeping positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 28 | Strengthening upper limbs |  |
 |
| 29 | Strengthening lower limbs |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible |  |
|
| 6 | For children with hemiplegia, this exercise stretches their affected arm with the help of their unaffected one and can be done using a stick shaped toy, standing or sitting |  |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
| 8 | Increasing tone in elbows |  |
 |
| 9 | Sitting balance |  |
 |
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 12 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 13 | Standing frame | 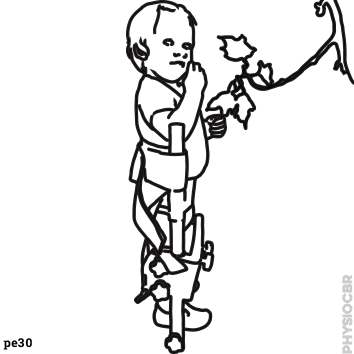 |
 |
| 14 | Standing frame alternatives |  |
 |
| 15 | Stretch the elbow by gently straightening the arm... if resistance occurs, pause before continuing when it has lessened |  |
 |
| 16 | Stretching on the wedge |  |
|
| 17 | Encourage hip flexion with supported walking |  |
|
| 18 | Move feet and knees through the available range |  |
 |
| 19 | Move feet and knees through the available range, depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required...if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range |  |
 |
| 20 | Encouraging arm movement, with reaching |  |
 |
| 21 | For floppy or decreased tone |  |
|
| 22 | Improving upper limb movement |  |
 |
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength |  |
 |
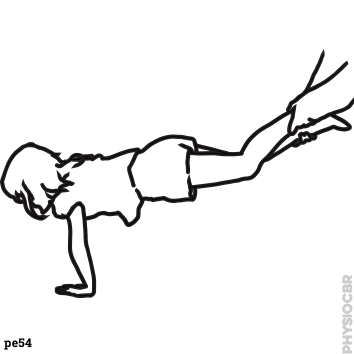
| 24 | Strengthening exercises for upper limbs | 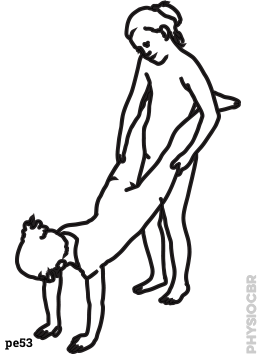 |
 |
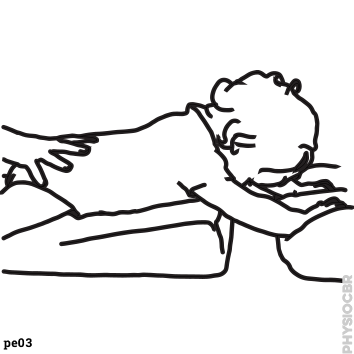 |
 |
||
| 25 | Resting positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 26 | Sleeping positions |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 28 | Strengthening upper limbs |  |
 |
| 29 | Strengthening lower limbs |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible |  |
|
| 1 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Move feet and knees through the available range |  |
 |
| 3 | Move legs through the available range, if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range. depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required |  |
 |
| 6 | For children with hemiplegia, this exercise stretches their affected arm with the help of their unaffected one and can be done using a stick shaped toy, standing or sitting |  |
|
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 11 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
| 12 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
| 20 | Encouraging arm movement, with reaching |  |
 |
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength |  |
 |
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible |  |
|
| 1 | Decreasing tone in wrists, stabilse child’s forearm whilst moving the hand |  |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Move legs through the available range, if strong resistance felt, wait for leg to relax to gain a little more range. depending on the level of spasticity, hold legs appropriate to where long or short leverage is required |  |
 |
| 6 | For children with hemiplegia, this exercise stretches their affected arm with the help of their unaffected one and can be done using a stick shaped toy, standing or sitting |  |
|
| 10 | Sitting balance on ball |  |
|
| 11 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
| 12 | Standing and reaching |  |
 |
 |
|||
| 23 | Positioning to encourage head and neck strength |  |
 |
| 30 | Handicap International have seen that the best way to improve a child's quality of life is to include them in the community as much as possible |  |
|