home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides
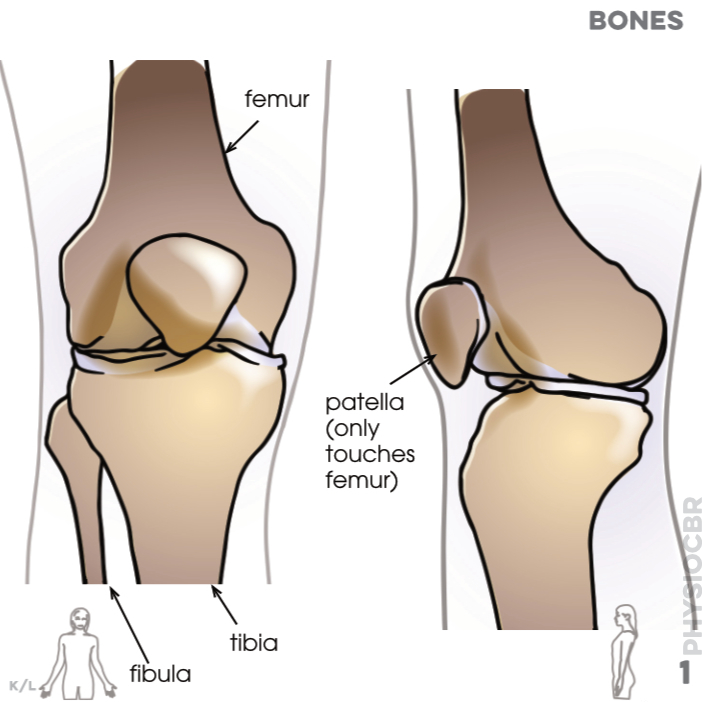
1. Bones: femur, fibula, tibia, patella only touches femur)
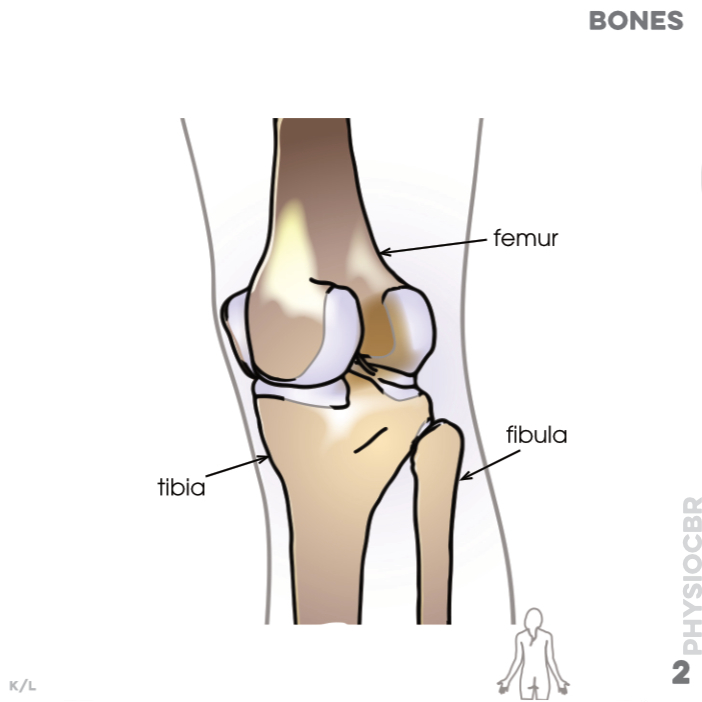
2. Bones: femur, fibula
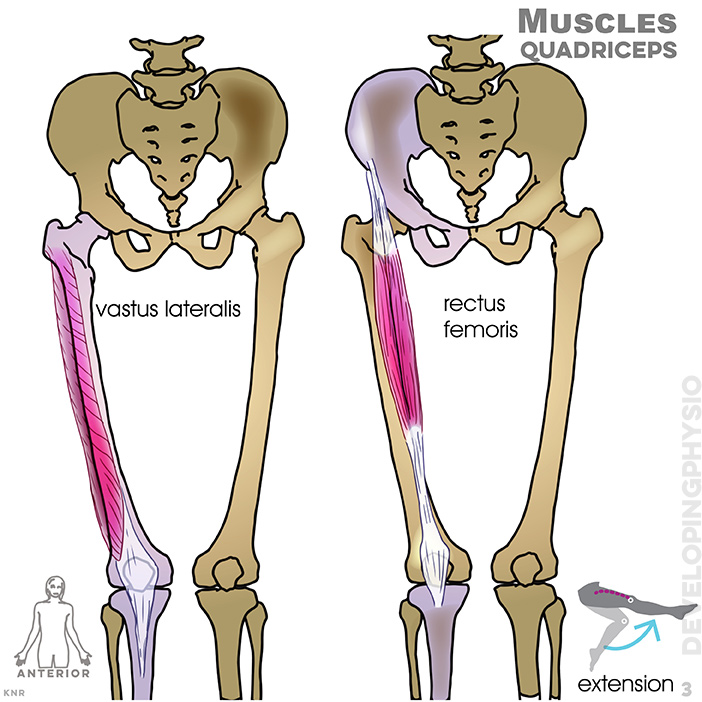
3. Muscles, quadriceps: vastus lateralis, rectus femoris
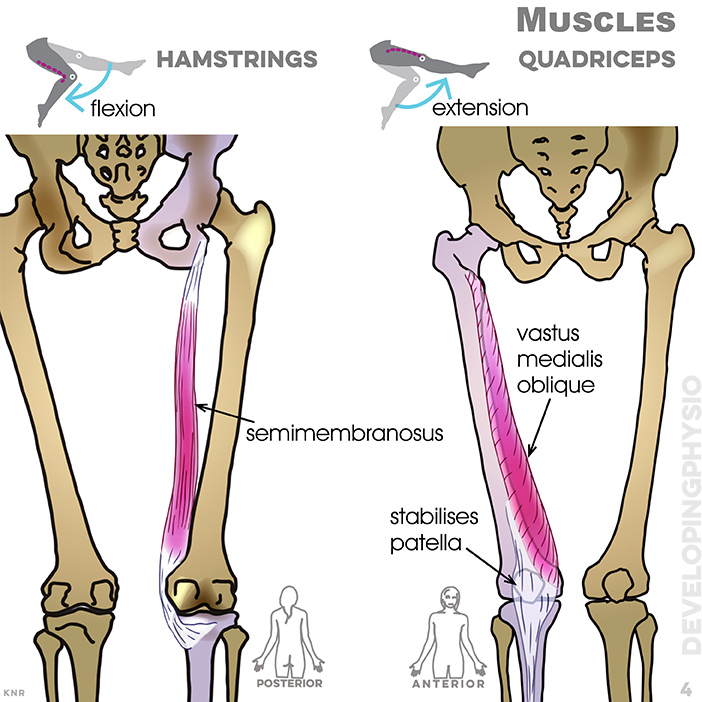
4. Muscles, quadriceps: semi membranosus, stabilises patella, vastus medialis oblique
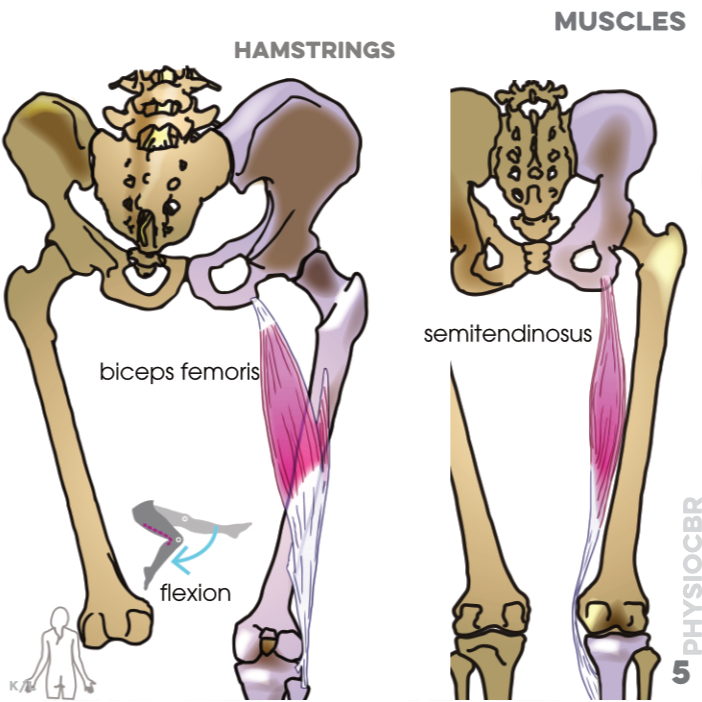
5. Muscles, hamstrings: biceps femoris, semitendinosus
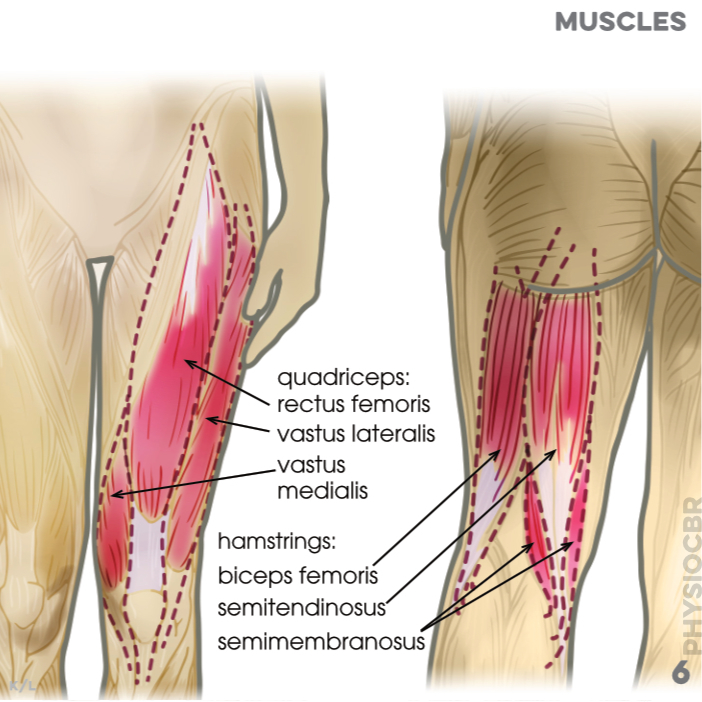
6. Muscles: quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis); hamstrings (biceps femoris, semi-tendinosus, semi-membranosus)
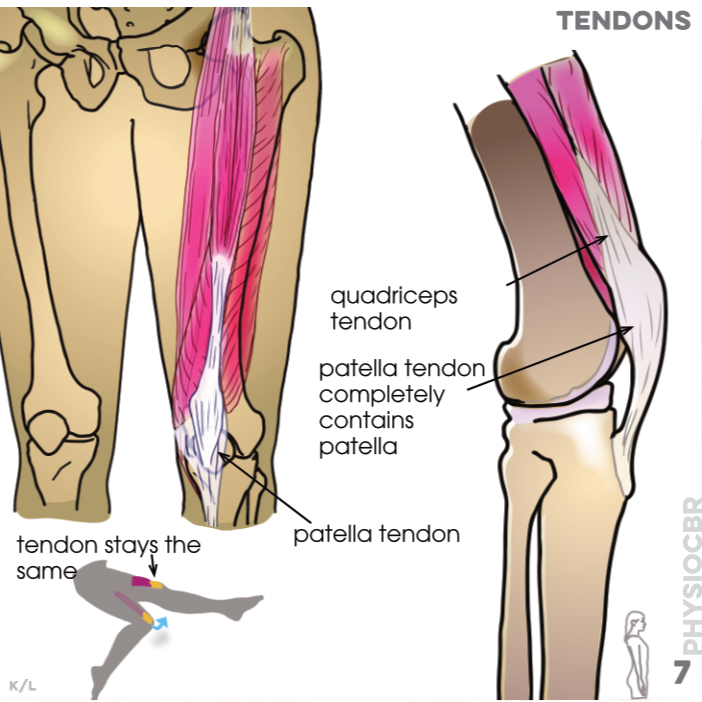
7. Tendons: quadriceps tendon, patella tendon completely contains patella (Tendons form part of the muscle that attaches it to bone so that, whilst muscles change in length, tendons do not)
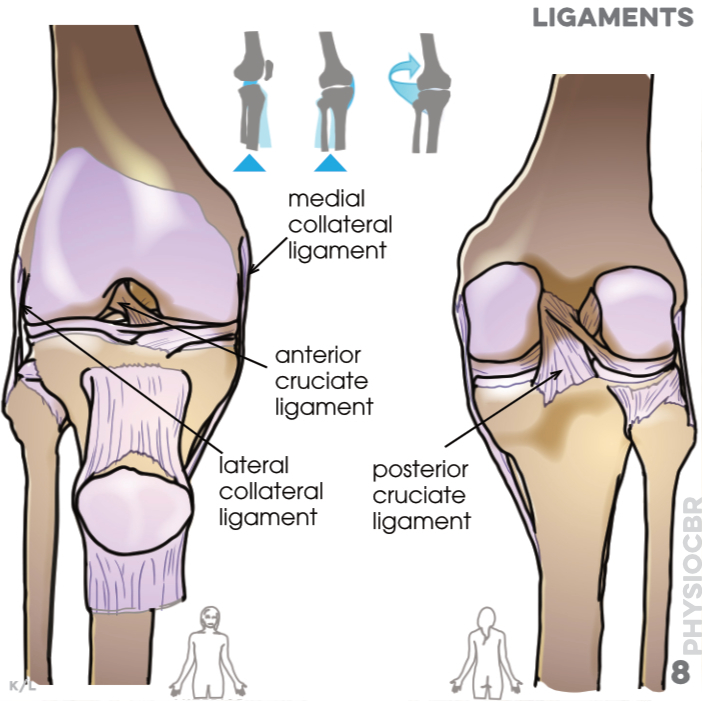
8. Ligaments: medial collateral, anterior cruciate, lateral collateral, posterior cruciate (Ligaments connect bones to stabilise and prevent excessive movement at joints)

9. Meniscus: lateral meniscus, medial meniscus (the meniscus is the cartilage disc that improves the contact surface and stability between the femur and tibia, acting as shock absorber, spreading the load over the entire joint)